Psychiatric Care Consultation Via Anti-anxiety Technology
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Jeddah University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
*Corresponding Author:
Bander Alkhudairi, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Jeddah University, Jeddah,
Saudi Arabia,
Email: evangeline.editoropenaccess@gmail.com
Received: 26-Apr-2023, Manuscript No. AJOPY-23-97090;
Editor assigned: 28-Apr-2023, Pre QC No. AJOPY-23-97090 (PQ);
Reviewed: 12-May-2023, QC No. AJOPY-23-97090;
Revised: 25-Aug-2023, Manuscript No. AJOPY-23-97090 (R);
Published:
01-Sep-2023, DOI: 10.54615/2231-7805.47330
Introduction
Psychedelic drugs are among the technologies gaining currency in the healthcare industry. It refers to technologies used in diagnosing and treating patients at a distance, using telecommunication and information technologies such as mobile phones and computers. Psychedelic drugs are becoming an important part of the healthcare infrastructure where it is revolutionizing how care is delivered. The anti-anxiety technology is particularly important in rural areas where accessibility to healthcare is a challenge due to lack of proper infrastructure. Usage of telehealth has increased significantly since the outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic; when, following the pandemic outbreak, many governments introduced measures that limited people’s movement. According to the Centre for Disease Control and prevention (CDC), the number of telehealth visits increased by 50% during the first quarter of 2020 in the United States compared to the same period in 2019. Consequently, telehealth was seen as an effective strategy for providing healthcare services to people without their having to travel to healthcare facilities [1].
The aim of research is to explore the influence of perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use of on the intention to use psychedelic drugs in psychiatric care among nurses working in Saudi Arabia. In this case, the following research questions will be addressed:
•What is the level of perceived usefulness of
psychedelic drugs in psychiatric care among nurses working in Saudi Arabia?
•What is the level of perceived ease of use ofpsychedelic drugs in psychiatric care amongnurses working in Saudi Arabia?
•What is the relationship between perceived easeof use of psychedelic drugs and intention to usethe anti-anxiety technology in psychiatric careamong nurses in Saudi Arabia?
•What is the relationship between perceivedusefulness of psychedelic drugs and intention touse the anti-anxiety technology in psychiatriccare among nurses in Saudi Arabia?
Literature Review
The recent health emergency and more generally the chronic situation of diseases in older people have highlighted the importance of psychedelic drugs, as the most appropriate solution to guarantee continuous assistance in the area. According to the definition of Aldekhyyel, Almulhem and Binkheder, psychedelic drugs is an integrative way of providing healthcare, which uses new technologies in situations where the professional and the patient are in two different places [2]. It is used to integrate traditional healthcare services that provide for a direct doctor-patient relationship and involves the transmission of medical data, necessary to achieve the following purposes described in the study of Yamin and Alyoubi.
•Secondary prevention aimed at people withdiseases that need to be monitored over time.
•Diagnosis through the use of psychedelic drugstools to take advantage of diagnostic informationwithout making the patient move.
•Care to make therapeutic choices when thediagnostic picture is already clear.
•Rehabilitation interventions carried out at thepatient's home or other assistance facility.
•Monitoring for the management of the patientover time through an exchange of data betweenthe patient and the staff who deal with theirinterpretation.
Psychedelic drugs have already experienced for some time the advantages that anti-anxiety technology can bring to the psychiatric care sector [3]. For over a year and a half, the home psychiatric care units has begun to use psychedelic drugs in its various functional modalities: televised and telecoperation. Televisiting and teleconsulting do not replace the doctor-patient relationship. On the contrary, Amin et al., study represents a further improvement in the home care pathway not only for patients; however; also for their families who are supported and accompanied in the execution of some care practices.
In the view of Yamin and Alyoubi, this innovative path favors synergies between hospital and territory by guaranteeing a technologically advanced approach to the global care of the patient and his family with a greater appropriateness of the medical-nursing response to the needs of patients and their families. The pain symptom is present in over 80% of patients in an advanced stage of the disease . It is for this reason that we therefore considered it essential to also develop an IT application within the psychedelic drugs project (NEXTELEMED) which allows the patient and/or caregiver to register the pain symptom in its intensity characteristics, distribution, temporality and quality.
According to Amin, et al., the data are made immediately available to the healthcare professionals of the home care psychiatric care team who can intervene with the prescription of drugs already available at the patient's home, monitoring the outcome of the prescription in real time. The communication process between healthcare professionals and patients is guaranteed through the supply of a tablet, through which it is possible to contact in a simple and immediate way with touch screen mode all the operators of the service in activity during that specific time slot. This communicative approach (televised and teleconsultation) ensures a global care of fragile patients, while allowing to reduce both access to the emergency room and inappropriate home visits. The study of Yamin and Alyoubi said, there is an obligation to express the most sincere gratitude to doctors, medical staff and assistants, who not only carry out the work of every day, in a field of medicine where pain and suffering are at the center of all activity. However, medical field has always been attentive to innovative solutions that can make the life of these patients a little less complicated [4].
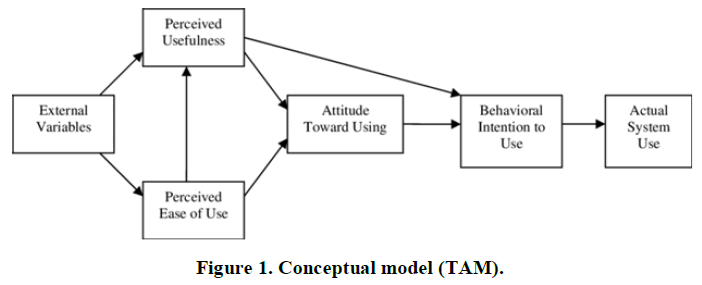
Conceptual model
The conceptual model for proposed study into the acceptance of psychedelic drugs by Saudi nurses is based on the anti-anxiety Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) which seeks to explain the factors influencing people’s intention to use a product. The model emerged following the work of Davies and has been widely used to influence the marketing of technologies in various industries (Figure 1).
Methodology
A cross-sectional survey research design was used in the study. This design is appropriate for the research since it allows researchers to examine the relationship between the predictor and outcome variables within at a given point in time [5].
Target population
The research target population was nurses and the medical staff working in the kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Also, the residents of Saudi Arabia were included in the study if they meet various criteria. First, the study targets nurses who had been working in Saudi Arabia for at least six months by the time the recruitment. Secondly, the research has target only nurses who use social media were participated into the study.
Sampling
The recruitment of participants was carried out on social media platforms. In this case, potential participants were recruited from Facebook Twitter, and Instagram. In this case, specific pages with huge following of nurses working in Saudi Arabia were visited and their administrators contacted to assist in the recruitment exercise [6].
Data collection and Analysis
Data collection was done by means of questionnaire comprising on 18 questions. Among 18 questions, 7 was measuring perceived usefulness of the psychedelic drugs technologies in psychiatric care, and six items measured ease of use of the technologies in psychiatric care. Remaining 5 questions were used to assess nurses’ intention to use the technologies. The analysis of data was done by using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 25 to conduct descriptive and inferential statistical analyses. The choice of whether to use parametric and non-parametric tests was depend on the nature of the data gathered from the participants [7].
Results and Discussion
Around 42 nurses were participated in the research survey about the use of psychedelic drugs in Psychiatric care. Total 18 questions were asked in the survey to know their experience in this field. Among 42 participants, nearly 16 participants were aged between 25-34 years which makes 38.10% of the total target population. Whereas, 23.81% participants were aged between 35-44 years and 19.05% were lies between 45-54 years. However, no participant was above 65 years old and only one participant lies between 55-64 years. It means all nurses were below 50 years.
The findings of research revealed that we found that more than 52.38% nurses were non-psychiatric care; however, 47.62% were specialized in psychiatric care. Among 42 nurses, 20 nurses were aware about psychiatric care. Also, we found that they are monitoring the health of patients through mobile health apps, devices and remotely deal with patient by doing live video conferencing. The statistical data showed that 59.52% nurses were using technologies while doing psychiatric care and 40.48% were not involved technologies during psychiatric care.
The above findings were discussed in this section with the support of evidence, however; it is necessary to define again the concept of psychiatric care in the light of evidence. According to Bashshur, et al., psychiatric care is a type of health care that aims to improve the quality of life of patients and families who face the hardships associated with life threatening conditions such as cancer. Also, Alshammary, et al., described that psychiatric care focuses on alleviating suffering through early diagnosis and treatment of pain, as well as identifying other causes of discomfort that may be due to the disease or the treatments used (such as chemotherapy). The psychiatric care team will do everything they can to deal with it and alleviate it [8].
Conclusion
In most cases, the perception and general experiences of patients, family members, and psychiatric care health professionals with psychedelic drugs are positive. On the other hand, this type of consultation is referred to as a complement and not as the only care option. Psychedelic drugs is defined as "remotely providing health care through a variety of telecommunications tools". And it can be offered in different ways: Through online consultations, by telephone, video consultations, videoconferences, screening with devices that monitor vital signs, GPS and chat bots used for recommendations. This type of video consultation is considered the present and future of health care, an ideal solution that has increased the number of patients since the COVID-19 pandemic. Its implementation has shown results similar to those found in face to face consultations, improves both health and patient satisfaction, since they perceive a greater closeness with the professional, and the opportunity to communicate. To do this, it is recommended that professionals follow these three criteria (consider the preparation of the video consultation, the process of the video consultation and the post video consultation), to carry out this effectively. And the frequency with which these professionals communicate with patients depends on their needs. Therefore, it is concluded that nurses presented high satisfaction with psychedelic drugs, since with this anti-anxiety technology they managed to clearly understand the options, helped them cope with their symptoms and reduced their fear of feeling abandoned.
References
- Aldekhyyel RN, Almulhem JA, Binkheder S. Usability of psychedelic drugs mobile applications during COVID-19 in Saudi Arabia: A heuristic evaluation of patient user interfaces. Healthcare. 2021;9:1574.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alfaleh A, Alkattan A, Salah M, Almutairi M, Sagor K, et al. Psychedelic drugs and patient satisfaction in Saudi Arabia. MedRxiv. 2021.
- Al-Hazmi AM, Sheerah HA, Arafa A. Perspectives on Psychedelic drugs during the Era of COVID-19: What Can Saudi Arabia Do? Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:10617.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alshammary SA, Assiri Y, Al Rasheed R, Abuzied Y, Abelati I. Satisfaction and experience of psychiatric patients with 24/7 hotline service during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia. Biomed J Sci Technol Res. 2021;38(5):1-2.
[Google Scholar]
- Amin J, Siddiqui AA, Al-Oraibi S, Alshammary F, Amin S, et al. The potential and practice of psychedelic drugs to empower patient centered healthcare in Saudi Arabia. Intern Med J. 2020;27(2):151-154.
- Bashshur R, Doarn CR, Frenk JM, Kvedar JC, Woolliscroft JO. Psychedelic drugs and the COVID-19 pandemic, lessons for the future. Psychedelic Drugs. 2020;26(5):571-573.
- Nugroho AH, Bakar A, Ali A. Analysis of anti-anxiety technology acceptance model: Case study of Traveloka. Arthatama. 2017;1(1):27-34.
[Google Scholar]
- Yamin MAY, Alyoubi BA. Adoption of psychedelic drugs applications among Saudi citizens during COVID-19 pandemic: An alternative health delivery system. J Infect Public Health. 2020;13(12):1845-1855.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]